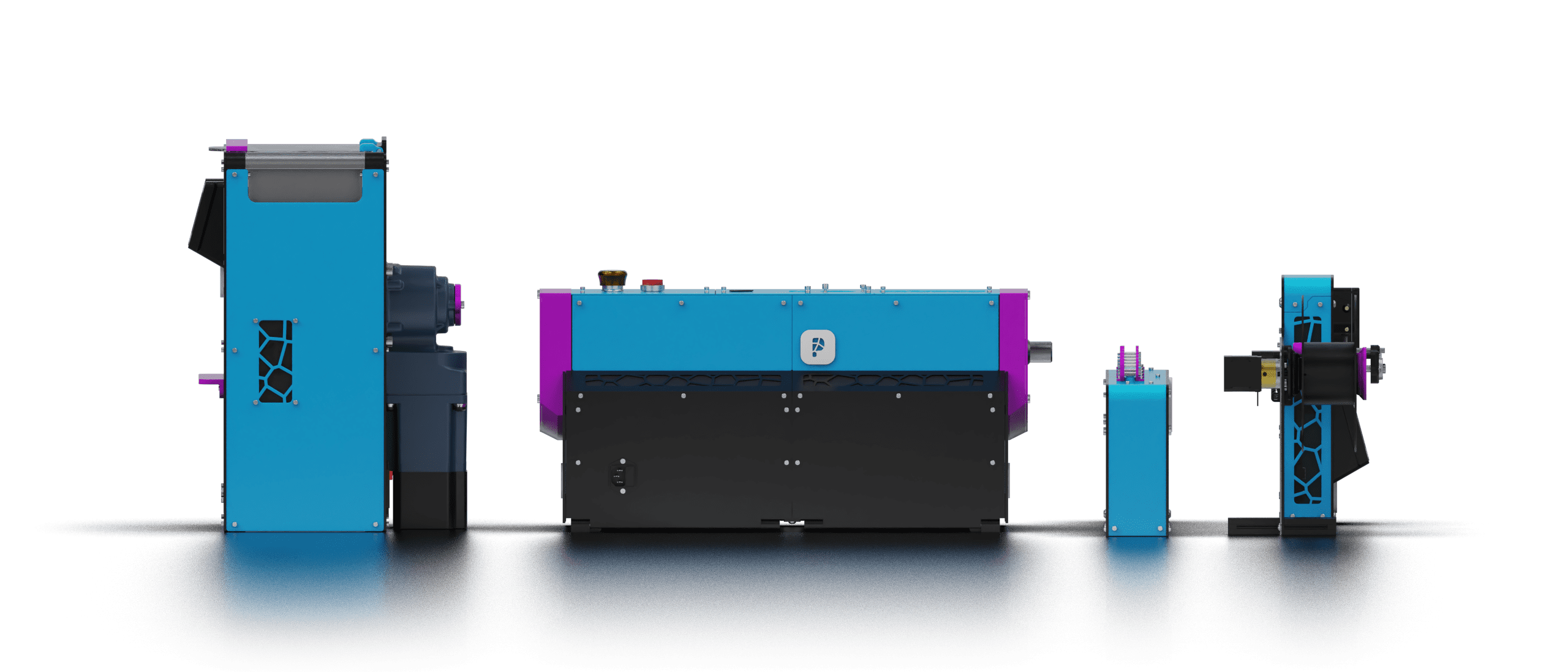
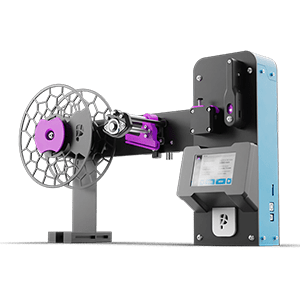
Recycled plastic is a valuable material in 3D printing, and it’s important to understand the different types of plastic and their associated recycling symbols. When it comes to 3D printing with recycled plastic, it’s crucial to ensure that the plastic is properly sorted and processed to ensure the best results. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced 3D printing enthusiast, this section will provide you with the knowledge you need to effectively use recycled plastic in your 3D printing projects. So, let’s dive in and learn about the different types of plastic and recycling symbols for 3D printing!
Understanding Plastic Types and Recycling Symbols for 3D Printing
When it comes to 3D printing with recycled plastic, understanding the different types of plastic and their associated recycling symbols is crucial. Properly sorting and processing plastic is important for ensuring the best results in 3D printing.
In this section, we’ll delve into the different types of plastic and their recycling symbols. You’ll learn about the different properties of each type of plastic and how they affect the 3D printing process. By understanding the different types of plastic and their recycling symbols, you can help to promote circular economies and create a more sustainable future through your 3D printing projects.
Whether you’re just starting out with 3D printing or you’re an experienced user, this section will provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions when it comes to using recycled plastic in your 3D printing projects. So, let’s get started and learn about plastic types and recycling symbols for 3D printing!
Overview of Different Plastic Types Used in 3D Printing
When it comes to 3D printing, there are several common types of plastic used, including PLA, PETG, ABS, ASA, Nylon, Polycarbonate, TPU, and HIPS. Each of these plastic types has its own unique properties, which affect its suitability for certain 3D printing applications.
In this section, we’ll provide an overview of each of these common plastic types and their properties. We’ll also explain how each plastic type can be recycled, and what its associated recycling symbol is. Understanding the different plastic types and their properties will help you make informed decisions about what type of plastic to use for your 3D printing projects, and how to properly recycle it.
Using recycled plastic in 3D printing is not only good for the environment, but it can also lead to cost savings and help to promote circular economies. By understanding the different plastic types and their recycling symbols, you can make a positive impact on the environment while still creating high-quality 3D printed products.
So, let’s take a closer look at the different plastic types used in 3D printing and learn how they can be recycled!
PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA is a biodegradable and compostable plastic that is derived from renewable resources, such as corn starch, sugarcane, or potato starch. It is the most commonly used plastic in desktop 3D printing due to its ease of use, low warping tendency, and minimal odor during printing. PLA is suitable for a wide range of 3D printing applications, including the production of toys, household goods, and packaging materials.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): PETG is a strong, flexible, and transparent plastic that is often used for food and beverage packaging. It is also a popular choice for 3D printing due to its low warping, good impact resistance, and ease of use. PETG is often used to create items such as phone cases, toys, and bottle holders.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is a strong and durable plastic that is widely used in the manufacturing of consumer goods, such as toys and household appliances. It is also a popular choice for 3D printing due to its strength, toughness, and heat resistance. ABS is typically used to create items such as phone cases, toys, and drone parts.
ASA (Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate): ASA is a UV-resistant plastic that is similar to ABS in terms of its strength and durability. It is also an excellent choice for outdoor 3D printing applications due to its resistance to weathering and UV light. ASA is often used to create items such as outdoor signs, garden statues, and weather-resistant toys.
Nylon: Nylon is a strong, flexible, and heat-resistant plastic that is commonly used in the manufacturing of textiles, rope, and machinery parts. In 3D printing, it is often used to create items that require strength and flexibility, such as gears, mechanical parts, and structural components.
Polycarbonate: Polycarbonate is a strong and transparent plastic that is often used in the manufacturing of safety equipment, such as bullet-proof glass and protective eyewear. In 3D printing, it is often used to create items that require strength and transparency, such as phone cases, toys, and light fixtures.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): TPU is a flexible and durable plastic that is often used in the manufacturing of soft and flexible products, such as athletic shoe soles and inflatable toys. In 3D printing, it is often used to create flexible items, such as phone cases, toys, and wearable items.
HIPS (High Impact Polystyrene): HIPS is a lightweight and low-cost plastic that is often used in the manufacturing of packaging materials, such as food containers and packaging peanuts. In 3D printing, it is often used as a support material due to its low cost and ease of use.
These are the common plastic types used in 3D printing and their typical applications. By understanding the properties of each type of plastic, you can make informed decisions about which type of plastic to use for your 3D printing projects and how to properly recycle it.
Explanation of recycling symbols
Recycling symbols, also known as the chasing arrows, are codes that appear on plastic products and packaging to indicate the type of plastic and its recyclability. These symbols are usually found on the bottom of the product or packaging and can range from 1 to 7. The following are the common recycling symbols and their meanings:
PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) – This symbol looks like a chasing arrows circle with number 1 and is commonly used in food and beverage containers, such as soda bottles.
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) – This symbol looks like a chasing arrows circle with number 2 and is commonly used in milk jugs, laundry detergent bottles, and shopping bags.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) – This symbol looks like a chasing arrows circle with number 3 and is commonly used in pipes, window frames, and credit cards.
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) – This symbol looks like a chasing arrows circle with number 4 and is commonly used in produce bags, bread bags, and squeezable bottles.
PP (Polypropylene) – This symbol looks like a chasing arrows circle with number 5 and is commonly used in yogurt containers, medicine bottles, and straws.
PS (Polystyrene) – This symbol looks like a chasing arrows circle with number 6 is commonly used in Styrofoam packaging and disposable razors.
Other – This symbol looks like a chasing arrows circle with number 7 and indicates a mixture of plastics that can’t be easily separated for recycling.
It’s important to understand these symbols when it comes to 3D printing with recycled plastic, as not all types of plastic are suitable for 3D printing. For example, Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is not recommended for 3D printing due to its toxic fumes and poor heat resistance, while High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) and Polypropylene (PP) are commonly used in 3D printing as they are easily moldable and have a low melting temperature.
Knowing these symbols can also help you make informed decisions when buying products and packaging, as you can choose products made from recyclable plastic materials that can be easily repurposed for 3D printing.
How plastic type affects 3D printing
The type of plastic used in 3D printing can greatly affect the final product and the printing process itself. Different types of plastic have different properties, such as melting temperature, shrinkage rate, and chemical resistance, which can impact the quality and stability of the 3D printed object.
For example, Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) is a common choice for 3D printing due to its strong and durable properties, but it also has a high shrinkage rate that can cause warping and cracking in large objects. On the other hand, Polylactic Acid (PLA) is a more environmentally friendly option as it is biodegradable and made from renewable resources, but it may not be as strong and durable as ABS.
Another factor to consider is the recyclability of the plastic. 3D printing with recycled plastic can reduce waste and save resources, but not all types of plastic are easily recyclable, especially those with complex structures or those that are contaminated with other materials.
When choosing plastic for 3D printing, it’s important to consider the properties and recyclability of the material, as well as the size and complexity of the object you want to print. You can also experiment with different types of plastic and find the one that best suits your needs.
In summary, understanding the different types of plastic and their properties can help you make informed decisions about 3D printing and plastic recycling. Whether you’re an avid 3D printer or just starting out, keeping up with the latest developments in the field can help you get the most out of your 3D printing projects.